Promote Biodiversity


Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD)
To gain a better understanding of Inventec's operational impacts and dependencies on nature, supporting subsequent operational strategy review and improvement, we have adopted the LEAP approach recommended by the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD). Inventec has implemented the LEAP framework—Locate, Evaluate, Assess, and Prepare—across its headquarters and established production sites in both Taiwan and Mainland ChinaNote 1, as well as within its supply chain. This process helps explore the interdependence between the plants and surrounding ecosystems, and the reliance and impact on nature.
Assessment Framework:LEAP
Step 1
Locate
Using Geographic Information System (GIS) spatial data overlay analysis, Inventec maps the locations of the assets, operating sites, and the supply chain. The analysis determines whether these areas overlap with biological habitats or protected areas and identifies if they have a direct relationship with Inventec’s value chain activities.
Step 2
Evaluate
Inventec evaluates the impacts and dependencies of the various activities on nature, determining whether the activity has a positive or negative impact.
Step 3
Assess
Further analysis is conducted to assess the nature-related risks and opportunities faced by Inventec. These findings are then integrated into the Company’s annual risk management processes.
Step 4
Prepare
Inventec prepares comprehensive strategic plans to respond to nature-related risks and opportunities.
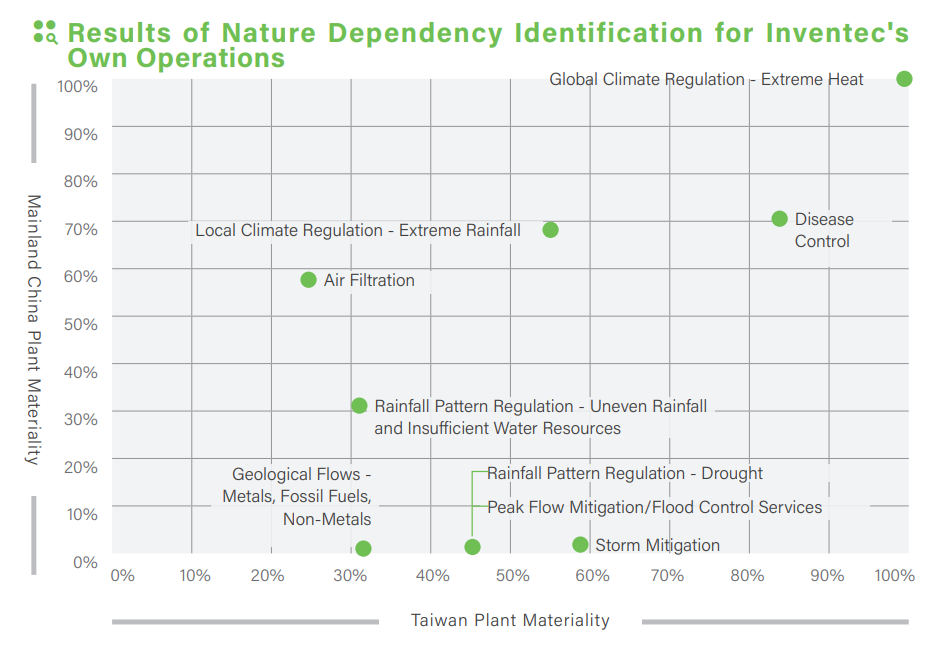
Inventec’s Own Operations: Nature Dependency Risk Identification Results for 2024
Through analysis, the Company identified five major nature dependency issues of concern for both its Taiwan and Mainland China plants from the 22 dependency categories outlined in the United Nations System of Environmental Economic Accounting (SEEA). These include global climate regulation - extreme heat, disease control, local climate regulation - extreme rainfall, air filtration (air quality degradation), and rainfall pattern regulation - uneven rainfall distribution. Among these, global climate regulation - extreme heat was identified as the most critical issue of concern.
Nature Dependency Risks and Opportunities in Inventec's Own Operations
Inventec monitors the dependency items identified for its own operations by setting corresponding indicators or early warning mechanisms. The Company also analyzes the risks and opportunities associated with each dependency category, evaluates their financial impacts, and formulates corresponding response strategies to control risks and capitalize on potential opportunities.
- Global Climate Regulation - Extreme Heat
- Local Climate Regulation - Extreme Rainfall
- Rainfall Pattern Regulation - Uneven Rainfall and Insufficient Water Resources
- Disease Control
- Air Filtration
- Rainfall Pattern Regulation - Drought
- Peak Flow Mitigation - Flood Control Services
- Storm Mitigation
- Geological Flows - Metals, Fossil Fuels, Non-Metals
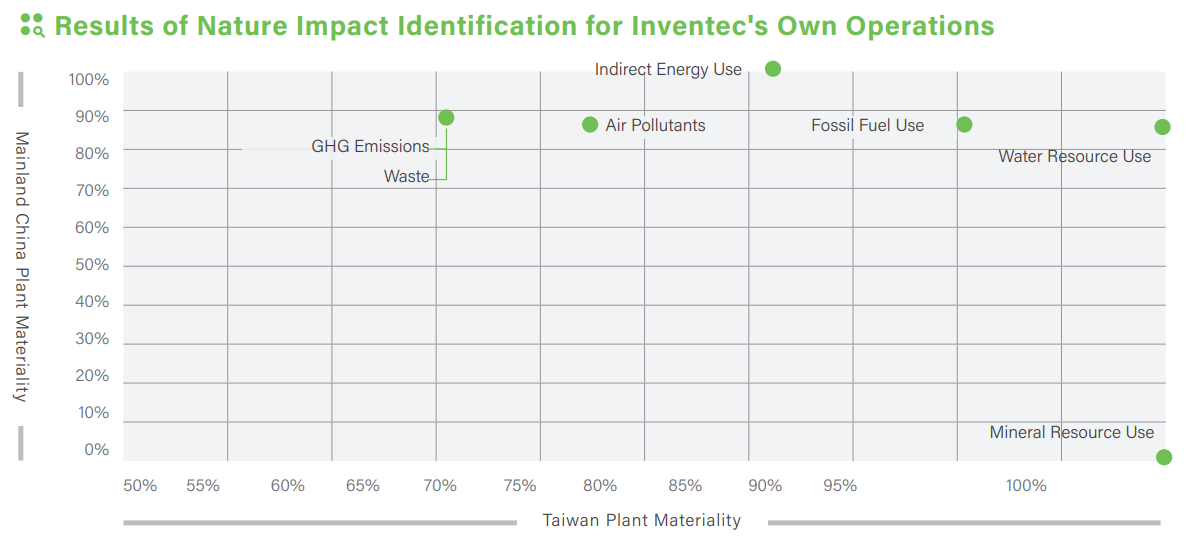
Results of Nature Impact Identification for Inventec's Own Operations
In terms of nature-related impacts, Inventec also conducted identification based on the 16 impact categories outlined in SEEA. Although the priority order of nature impact categories identified by the Taiwan and Mainland China plants differed, the main areas of concern encompassed six material nature impact categories: water resource use, indirect energy use (primarily electricity), fossil fuel use, air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation.
Nature-Related Impact Risks and Opportunities in Inventec’s Own Operations
Similar to the identification of nature dependencies, we have established corresponding indicators for each identified nature-related impact to thoroughly analyze the associated risks and opportunities. Concurrently, we evaluate the potential financial implications of these impacts and formulate effective response strategies.
- Indirect Energy Use
- Water Resource Use
- Fossil Fuel Use
- Waste
- GHG Emissions
- Air Pollutants
- Mineral Resource Use (e.g., Metals, Non-metals)
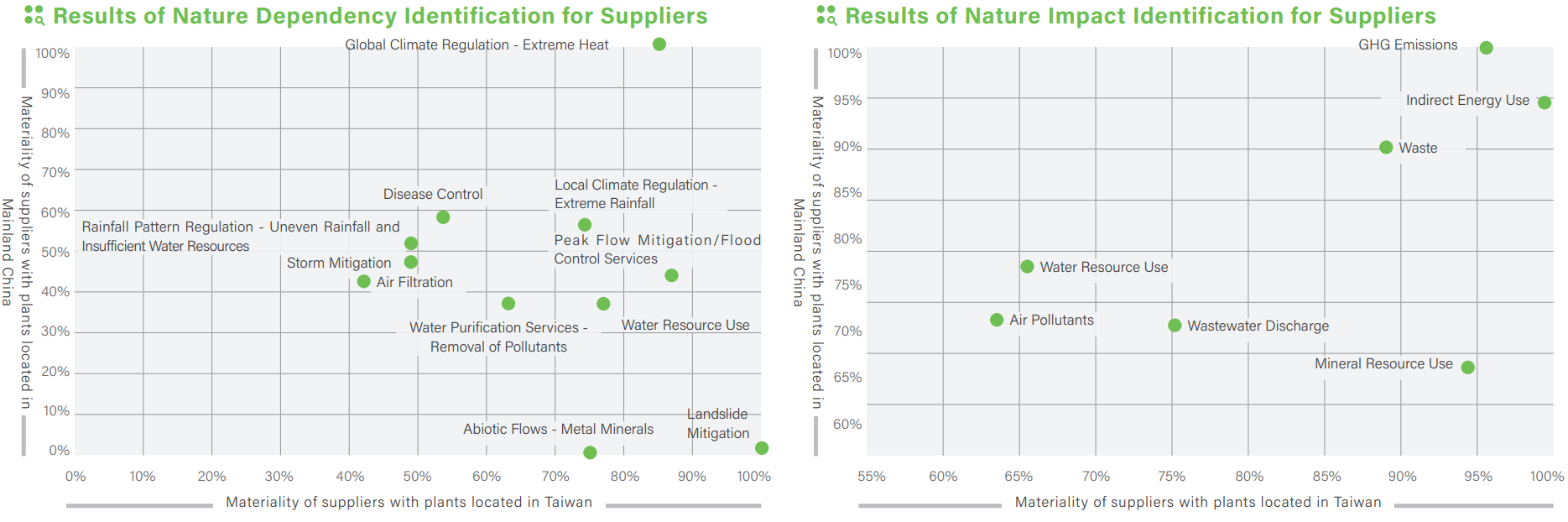
Results of Nature Dependency and Impact Identification for Suppliers
To effectively understand the nature-related risks and impacts across its supply chain, Inventec conducted a nature dependency and impact survey targeting suppliers with manufacturing sites in Taiwan or Mainland China. The identification results revealed that suppliers commonly face the following key nature dependencies: global climate regulation - extreme heat, local climate regulation - extreme rainfall, peak flow mitigation - flood control services, and water resource use. Suppliers with plants in Taiwan were particularly concerned about global climate regulation - extreme heat, water resource use, and peak flow mitigation - flood control services, while those in Mainland China, in addition to global climate regulation - extreme heat, also focused on local climate regulation - uneven rainfall and disease control. Among the categories of nature impacts, suppliers with manufacturing sites in Taiwan or Mainland China commonly identified indirect energy use (electricity), greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation as key impacts on nature. Taiwan-based suppliers were more concerned about mineral resource use and wastewater discharge, whereas Mainland China-based suppliers placed greater emphasis on water resource use.
Xitou Cloud Forest Biodiversity Initiative
Globally, only about 1% of forests are classified as cloud forests. Taiwan, as a high-mountain island located at the intersection of subtropical and tropical zones, possesses extremely rich montane cloud forest resources. "Fog" is a crucial source of moisture for the ecosystem, providing non-rainfall water supplementation while reducing excessive solar radiation, thus offering a protective function for the forest ecosystem. This "fog umbrella" helps create an environment suitable for the survival of diverse species and is of critical significance to the biodiversity of cloud forests. However, long-term observations show that the Xitou cloud forest, situated in a typical subtropical cloud forest belt, exhibits a downward trend in the frequency of fog formation. In addition to global warming, the annual influx of nearly two million visitors and the growth of surrounding recreational industries may also lead to localized warming and reduce the frequency of fog formation, posing a potential threat to biodiversity.
To protect Taiwan's mountain forests and address the biodiversity crisis, the National Taiwan University Experimental Forest and Inventec Group have joined hands in a collaborative e ort. Inventec sponsored research funding and provided software and hardware equipment such as edge computing devices and infrared sensing technology. AI-powered intelligent image algorithms are used for object detection and image analysis to help investigate the root causes of fog reduction. Through this cross-sector collaboration, both parties target to identify the environmental threats leading to fog reduction and develop effective solutions to safeguard Taiwan's cloud forest ecological resources, enabling the sustainable coexistence of rich and diverse mountain forests and natural resources with humanity. Inventec believes that enterprises should not only aim for profit but also leverage their technological advantages to fulfill social responsibility, serve humanity, and protect the ecology and overall environment, thereby practicing sustainable values through concrete actions.
Project result: AI Heads to the Mountains! Smart Technology Launches Cloud Forest Conservation Initiative
Wetland Project
In the area of ecological conservation, Inventec has collaborated with the Wild Bird Society of Taipei for years to promote the Guandu Nature Park Ecological Education Program. Employees have also actively participated as conservation volunteers at Guandu wetlands, and Inventec has sponsored various ecological conservation initiatives targeting the park's pond ecosystems.
To promote the vision of harmonious coexistence between humans and nature, the Inventec Group Charity Foundation has continuously adopted and supported the nationally significant Guandu Nature Park wetland for 13 consecutive years since 2012. In 2024, a total of 98,734 visitors explored and experienced the beauty of the Guandu wetlands, marking a significant milestone in ecological conservation efforts.
Furthermore, to advocate for the protection of these precious wetland environments and to root the concept of biodiversity in young minds, Inventec sponsored five sessions of the wetland environmental education program in 2024, benefiting 139 teachers and students from remote area schools. This initiative highlights the significance of the Guandu Nature Park as a representative ecological conservation site in the Greater Taipei area. From 2013 to 2024, Inventec has cumulatively supported 89 sessions, enhancing the ecological experience for 2,378 participants.

Environmental Education
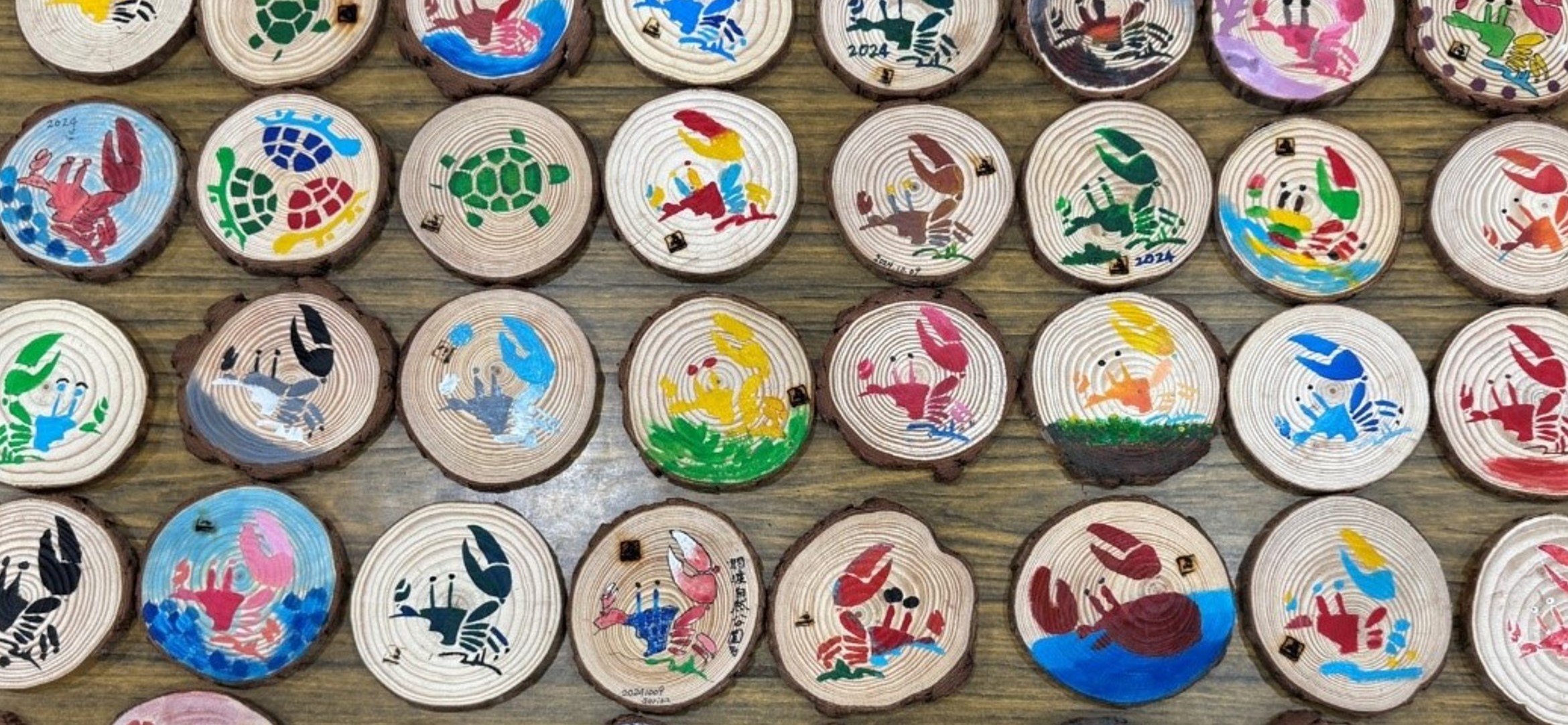
On October 9, 2024, Inventec held the "2024 Relay of Love Volunteer Day", with 39 passionate Inventec volunteers participating in public service activities at the nationally significant Guandu wetlands. These volunteers handcrafted wooden coasters, which were gifted to students from remote areas. Meanwhile, Inventec expanded the impact of inclusive care by sharing “Angel Lunch Boxes” from the Children Are Us Bakery & Restaurant.
Volunteer activities included wearing wading gear or using gardening tools to maintain the ecological ponds adopted by the Foundation. In addition, volunteers personally crafted 40 wooden coasters as eco-friendly gifts for students in remote areas who participated in the wetland environmental education program sponsored by the Foundation—allowing these students to experience environmental education while receiving meaningful ecological tokens. On the same day, 14 Angel Lunch Boxes from the Children Are Us Bakery & Restaurant were presented to the partners who participated in the Volunteer Day event, jointly taking practical actions to support and care for sheltered workplaces.

▲ Inventec volunteers handcrafted wooden coasters as eco-friendly gifts for children in remote areas.
Volunteer Activity Satisfaction Score: Average 9.32/10
“It’s been 25 years since I joined Inventec, and this was my first time participating in the Volunteer Day event. I felt fulfilled and deeply moved. The company has been quietly contributing to public welfare, and seeing our teammates work together to complete the tasks was truly amazing. Inventec is the best company!”
“Combining this with activities for underprivileged schoolchildren organized by the Guandu Nature Park also fulfills our goal of social service.”




